Methods of contouring :-
(1) Direct method
(2) Indirect method
(1)Direct Method : The method in which contouring of the points of required elevation are directly located on the ground with help of a levelling instrument (or a hand level or a abney's level ) is called direct method .
Use of direct method:-
- for small areas and when great accuracy is required .
Contouring by direct method is done by any of the following methods:
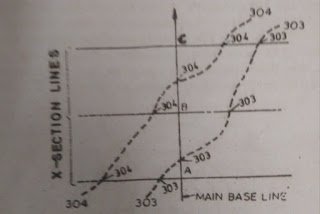
(1) By Selecting a long main line and then taking cross section at suitable intervals
(2) By radial Method
(3)By use of plane table with levelling operation
(1) Direct method by selecting a long main line :
In this direct method, contouring is done along the selected base lie and along the selected cross sections.
Procedure of contouring by selecting a long main line :
(a)A long main or base line is selected on the ground of area of which the contour map is prepared pegs are then driven at an interval of 10m or 15m or 20m depending upon the importance of survey .
(b) Cross section at right angles to the base line are drawn at pegs fixed in & above extending both ways of the base line up to the length sufficient to include the required area to be contoured.
(c) The level is then set up near the middle of the area and the reading of staff kept above the bench mark (may be permanent or temporary ) is taken. Suppose the R.L bench mark is 302.00m and the staff reading is 2.75 m. The level of the line of collimation is then (302+2.75=304.75 m)
(d) Now decide the elevation of the required contour to be located directly on the ground .Let it be 303.00 .The staff reading which should be read through the telescope of the level at the above setting reading bubble in the center, will have an elevation of 303.00 The points of R.L 303.00 are located on the each cross sectional line moving the staff on the each cross section line till the staff reading bisected on each points 1.75m. The position of such point is recorded in the field note book by measuring distance from the main base line from the main pegs such as A,B ,and C etc. shown in fig to the left or right in order to facilitate plotting later on
(e) Now suppose the next contour to be located has elevation 304.00 .The staff reading required to locate points on the cross sections will be 304.75 -304.00= 0.75 m.
The process is repeated till all the points of required contour level are located from one setting. The level is then shifted to other setting and above process is repeated till the whole area is contoured .
Uses:
The method of contouring by cross section is suitable for determining contours over a long but narrow strip as in the case of roads ,railways and canals etc. advantage being that the positions of the required points can be easily traced along the cross section .
By Radial Method : In this direct method contouring is carried out by following radial lines drawn from a common point approximately in the center of area .
For small areas where a single setting in the Centre can command the whole area , this method is the most suited .Radial lines are ranged from a common centre by theodolite or a compass and their relative positions being fixed by measuring the angles between them .Temporary bench mark is first established at the Centre and the contour points of required elevation are then located on these lines as described above. The position of the points are found by measuring their distances from the Centre setting along the radial lines. They are then plotted on the plan and the contours drawn by joining all the corresponding points as shown in fig
Direct method by use of plane table :In this method there is no necessity of having a main base line and taking cross sections
Procedure :
(a)Plane table is set up at a convenient place in the area to be contoured. The level is then set up near to the plane and the height of line of collimation is found by taking a staff reading on permanent or temporary bench mark of known reduced Level (R.L)
(b) The staff reading is calculated for locating contours of known elevation. The leveller then directs the staff man to more forward, backward, sideways so that the calculated staff reading kept over a point of required elevation is bisected by the line collimation.
(c) as soon as the positon of the required point of known elevation is located the distance of this point is measured from the centre of plane table .A ray is drawn by means of an alidade in the direction of staff point and the point is located on the plane table sheet at required scale and the R.L written along the point .
(d) The above procedure is repeated to locate other points on the ground and on the plane table. The points of the same elevations are then joined to draw the contours.
Indirect method :
The method in which spot levels taken on already fixed over the entire area, their respective R.L written against each point in the plan drawn to scale and contour lines drawn by interpolation is called direct method.
Uses:
This method is used in all kind of survey being cheaper ,quick and less tedious compared to direct method of contouring .
Contouring by Indirect method is done by any of following method:
(1) By squaring method
(2) By Cross Sections method
(3) By Tachometric method
(1) By square method :
This method is usually used when the area to be contoured is small and without too many undulation .In this method the whole area to be contoured is enclosed by setting out a big square or a rectangle .
This is big square or rectangle is divided into series of squares or rectangle , the sides of which may vary from 3m to 30m depending upon .
(a) nature of ground
(b) The contour interval
(c)the accuracy of the work required .
 |
| Square method |
The corners of the of the square or rectangle are marked with pegs and each peg is numbered so as to facilitate plotting the position of the pegs afterwards.
Preferably the size of the square or rectangle may be uniform however, it need not be same size throughout depending upon the nature of the ground .With respect to known bench mark , the elevations of the ground at the corners of the squares or rectangles are determined with a level when required .The field work is then plotted on a sheet of paper to required scale and the reduced levels of all the corners and other points are written against each near them. The contours of the required elevation are drawn by the method of interpolation as shown fig .two unique points L and M represent depression and hill respectively .this method gives fairly accurate results for a small area and the contour interval may be kept small from 30cm to 60 cm.
(2) By Cross Sections Method : This method is most suited to route surveys. Cross sections are run transverse to the centre line of railway , road or a canal etc. The cross section lines need not necessarily be at right angles to the centre line, they can also be inclined at any angle to centre line as per requirement.
 |
| Cross Section Method |
The spacing of the cross- section depends upon the character of the ground , the contour interval and the purpose of the survey. Pegs are then driven at regular interval and each cross-section on the both sides of the centre line .Levels are taken over these points and there elevations calculated with respect to any known reduced level near the area .The cross -sections and the points are plotted on the plan. The reduced level of each point is recorded and contour lines are then drawn by interpolation as shown in fig 1.8.The spacing of cross sections may be 20m to 30m in hilly area and 50m to 100m in flat country .
(3) By Tachometric Method :
In this method instrument known as tachometer is used . A tachometer is theodolite fitted with diaphragm having two stadia wires, one above and other below the central wire. The staff intercept is then calculated by taking the difference between the readings of the upper and lower stadia wires. Horizontal distance is determined by multiplying this intercept with the stadia constant of the instrument which is usually 100 .The horizontal distance thus need not be measured , since the tachometer provides both horizontal as well as vertical control
This method is most suited when a contour map of hill is required . also tachometer can command more area and thus it is cheap and economical comparatively .
From each of the traverse station a number of radial lines are set out at a known angular interval and pegs are driven on these as per requirement . The elevation and the horizontal distance of each point is determined and recorded . The survey is plotted on the plan and contour lines are the interpolated as usual .
.
Difference Between Direct and Indirect Method of contouring .
Direct Method Indirect Method
(1) It is slow and laborious method (1) It is quick as well as less laborious .it is
but it is most accurate not so accurate but is cheap
(2)It is used for small area (2) Used in all kinds of surveys and large
where great accuracy is required areas where great accuracy is not the main criteria
(3) It is not very useful for hilly (3)In hilly areas tachometric method of contouring
areas gives better result.
(4)Calculation work is more since (4)By using tachometer area commanded from one
control from one set up of the set up is more and hence less calculation work.
level is less and also the staff reading
,requirement at each point
to be worked out
Methods Of Interpolating Contours:-
Interpolation of contours is the process of spacing the contours proportionally between the plotted ground points which have been established by indirect methods of contouring .
There are three methods of interpolating contours :
(a)By Estimation Method : The method in which positions of contour points between ground points estimated roughly and the contour line drawn through these points is called estimation method .
(b) By Arithmetic Calculation Method :The method in which the interpolation of contour done by mathematical calculation is called arithmetic calculation method
(c) By graphical Method : The method in which interpolation of contour done by use of graph peper is called graphical method
Contour Gradient :A contour gradient may be define as a line joining the points on different contours along the same gradient .


Please do not Enter Spam link in comment box ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon